Understanding RC Airplane Controls
As a newcomer to the radio control flying hobby, learning about the primary rc airplane controls of your new plane is key to becoming a good pilot, and getting the most out of your model.
The number of controls required differs between planes; the simplest rc airplanes will have just one single control while the more complex planes may have five, six or more. Your 'average' rc plane will have three or four controls, this is by far the most common number, especially on a trainer plane.
Incidentally, any controllable function of a radio controlled model is referred to as a channel. An rc airplane with control to, say, four functions will be called a 4-channel plane.
Primary Airplane Controls
RC airplane controls are, of course, the same controls as those found on real planes and they control the model in exactly the same way.
The four primary controls of an rc plane are, in no particular order, throttle, elevator, ailerons and rudder. The elevator, ailerons and rudder are known as control surfaces and the picture below shows where these are located on a plane:
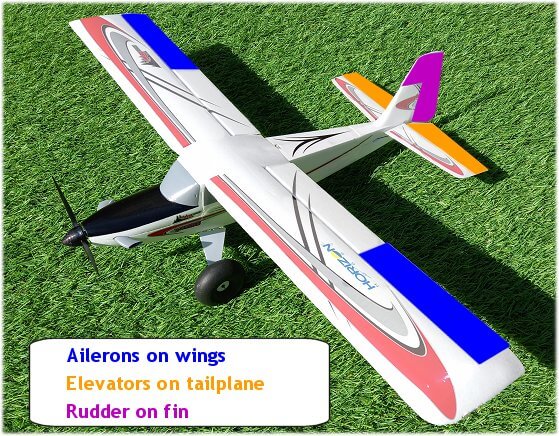

Above: location of ailerons, elevators and rudder on an rc plane.
The control surfaces are the hinged sections of the flying surfaces (wing, tailplane and fin) and each control surface moves - up and down in the case of elevators and ailerons, and left and right in the case of the rudder.
This movement alters the airfoil shape of the entire flying surface, and thus changes the amount of lift/downforce/sideforce being generated by that flying surface. The airplane responds to these changes, resulting in a change in attitude and/or direction. By attitude, we mean the plane's orientation in relation to the horizontal. For example, if the plane is pointing upwards it has a nose-up attitude.
Control surface movement is called deflection or throw. The very crude (sorry!) animation below shows how a control surface moves in relation to its parent flying surface:

Which Controls do What?
Now you know where the primary rc airplane controls are located, let's take a look at each one...
Throttle
 Throttle controls engine speed and hence how fast or slow the propeller spins. In turn, this changes the amount of thrust produced.
Throttle controls engine speed and hence how fast or slow the propeller spins. In turn, this changes the amount of thrust produced.
On a glow plug (or petrol) rc airplane engine the throttle works the same as any internal combustion engine throttle, by changing the amount of fuel and air that enters the combustion chamber of the engine.
The carburettor is operated by a single servo connected to the venturi of the carb, which opens and closes (thus changing the fuel/air mixture) in response to your throttle stick movements on the transmitter.
On an electric rc airplane the throttle is usually referred to as motor power rather than throttle. Very basic electric rc planes (i.e. toy ones) might not have proportional control to motor power but just a simple on/off switch instead.
Electric planes that do have proportional control to motor power have an electronic speed control, or ESC, that controls power to the motor in direct response to your Tx stick movements.
In the air throttle not only controls the forward speed of the airplane but also, more importantly, the rate of climb and descent, because different amounts of lift are generated at different airspeeds. For example, if your landing approach path is too low you can make the airplane rise slightly without changing speed much, simply by opening the throttle instead of using up elevator. Conversely, closing the throttle will cause the airplane to sink before the speed reduces.
Using throttle/motor power in this way is the correct way to fly your rc airplane, but many pilots use the elevator to control altitude and rates of climb and descent rather than engine speed.
Elevators
The elevators are the hinged section of the tailplane, or horizontal stabiliser, at the very rear of the airplane and are the single most important control surface. They directly effect the plane's airspeed.
Elevators control the horizontal pitch attitude of the airplane, in other words whether the nose of the plane points upwards or downwards.
When elevators are deflected upwards the plane's nose is forced to point upwards, and with the elevators deflected downwards then the nose is forced downwards. This resulting nose up/nose down pitch attitude comes about as the upward/downward deflection of the elevators changes the amount of down force being generated by the tailplane.
It's worth noting that a plane can still fly level, or even be descending, with a very nose-up attitude but a nose-down pitch attitude will always result in the plane entering a dive, thanks to our friend gravity!
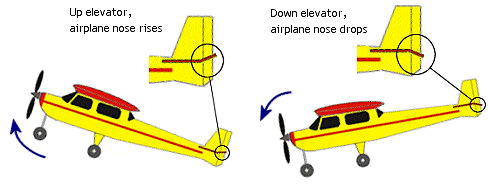
Elevators should be used in conjunction with rudder and/or ailerons when making a turn, to maintain altitude during the turn and also to get the plane to bank during the turn.
Ailerons
Not all rc airplane controls include ailerons, in fact many 3-channel trainers use rudder instead. But where fitted, ailerons control the roll of the airplane about its longitudinal axis (imagine a straight line running through the centre of the fuselage, from nose to tail).
Ailerons work in pairs and are found on the trailing (rear) edge of the wing, and they work opposite to each other i.e. when one aileron moves up, the other one moves down and vice versa.
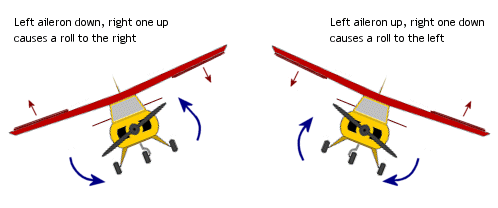
Ailerons work by changing the amount of lift generation over the wing.
As an aileron moves upwards so it disrupts the smooth airflow over the wing surface and so lift is reduced slightly on that wing. Over on the other wing the aileron moves downwards and increases lift slightly. As a result, the airplane tilts and hence rolls towards the side that's experiencing less lift.
When up elevator is applied at the same time as ailerons, the airplane is pulled round in to a banked turn; the ailerons cause the plane to roll and the up elevator causes the nose to pitch round in that direction.
Ailerons are used in all aerobatic maneuvers that involve a rolling motion.
Rudder
The rudder is the hinged section of the fin, or vertical stabiliser, at the rear of the airplane.
It's used for directional control by changing the yaw of the airplane, and works in the correct sense i.e. moving the rudder to the left causes the airplane to turn left and vice versa.
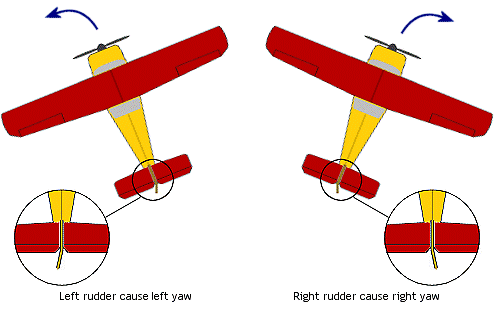
Applying rudder makes the nose of the airplane point to the left or right, but rudder alone does not make the airplane roll like ailerons do. It's actually the dihedral, or the upward 'V' angle of the wing when viewed from the front, that makes the plane roll when rudder is applied; a plane with very little or no dihedral will have a much flatter turn when rudder is applied. This is all to do with a natural force called Dihedral Effect.
Planes with ailerons require less dihedral than planes that rely solely on a rudder for turning, as the ailerons make the plane roll.
Rudder is also very important on the ground, it's the one control that will keep your rc airplane tracking straight during a take off run or landing roll, if your plane isn't fitted with a steerable nose or tail wheel.
Other RC Airplane Controls
Other important controls found on more complex rc airplanes include flaps and retractable landing gear, or 'retracts'.
Flaps
Flaps are located on the trailing edge of each wing, between the aileron and fuselage. They're used to generate more lift at slower flying speeds and, at greater deflection, to slow the airplane down close to landing by causing excessive drag.
Unlike ailerons, flaps are connected in such a way that they both drop exactly the same amount together so as not to upset the roll attitude of the plane when they are deployed.
Flaps are typically operated with a toggle switch on the transmitter, and modern transmitters will likely have the option to set flap speed, so the flaps can be made to move down slowly as on a full size plane.
When a lesser amount of flap is used (for example, 10° or so) it's quite common for the airplane to pitch upwards as soon as the flaps are lowered. This is a result of the extra lift being generated and the pilot needs to be aware of this happening before he activates the flaps.
The trick here is to use elevator compensation, either manually or have it mixed in the radio so that when flaps are lowered, the elevator automatically drops slightly to help maintain the plane's path.
Split flaps are a type of flap typically found on many warbirds. With split flaps, the flaps lower from beneath the upper surface of the wing i.e. the upper and lower wing surfaces are split to form each flap.

Retracts
Retractable landing gear (undercarriage) is landing gear that folds away into the airplane's wings or fuselage once the plane has taken off.
Retracts are often used on larger rc airplanes, particularly scale models where the real airplane has retractable undercarriage. Larger non-scale airplanes can also have retracts, particularly competition rc airplanes where it's necessary to reduce the amount of drag on the plane in the air. Obviously an airplane with no landing gear hanging below it experiences a lot less drag than one with.
Retracts can be operated mechanically by a servo, driven by compressed air or electric worm-drive. The retraction of the landing gear is operated by a single switch on the transmitter, typically either on the 5th or 6th channel.
Control Surface Mixing
Some rc planes are designed in such a way that they cannot have separate controllable surfaces. Planes with a large delta wing and no tailplane, for example, such as my Weasel shown below:

When this is the case control surface 'mixing' is necessary and this is only possible on computerised rc transmitters that offer a mixing capability. These days, most radios offer at least basic mixing.
The secret of control surface mixing is that each control surface must be able to work together with its partner surface (i.e. both up and down together), as well as opposite to (i.e. one up, one down).
Common control surfaces that are mixed ones include...
- Elevons, whereby elevators and ailerons are combined together on a flying-wing or delta type plane. Elevons move up and down together, as elevators do, and individually, as ailerons do. In short, one pair of elevons does the job of elevators and ailerons.
- Ruddervators are the control surfaces found on 'V' tail airplanes. Like elevons except that rudder and elevator control is combined, rather than aileron and elevator.
- Flaperons are control surfaces that mix the actions of ailerons with flaps. In other words, one pair of control surfaces along the trailing edge of the wing take on the job of aileron control and flap control, when needed.
- Spoilerons are, in effect, the inverted version of flaperons. Spoilers operate by the control surfaces moving upwards as opposed to flaps that drop down. When spoilerons are deflected, the amount of lift is reduced and so the glider's rate of descent quickly increases, enabling the pilot to land it in a smaller space.
There are other types of rc airplane control mixing too, but those listed above are by far the most common that you'll encounter.
RC Channel Mixing
Channel mixing is another type of mixing supported by modern computer radios, whereby two separate channels can be mixed to operate together.
A common example of channel mixing is an aileron and rudder mix; a small amount of rudder is automatically applied when you operate the ailerons. The purpose of this is to produce a cleaner turn and can prevent the effects of adverse yaw, a common situation whereby the tail drops during a turn due to increased drag over the higher wing. Aileron Differential is the 'mechanical' answer to this issue.
Another example of a popular channel mix is to have elevator compensation with flap operation. As the flaps are lowered, the elevators automatically deflect downwards to counteract the natural tendency for a plane to pitch up as flaps are lowered (a result of extra lift being generated by the lowered flaps).
Proportional RC Airplane Controls
You might see the word proportional when looking at radio control systems.
By proportional control, we mean that the control surfaces respond directly to how much you move the stick of your transmitter. In other words, if you only move the stick a small amount then that channel will only respond a small amount. Moving the stick to the maximum position will move that channel to its maximum.
Apart from the cheapest rc toys, all modern-day radio control systems are proportional. Non-proportional functions of an rc model or toy will be simple 'on/off' or 'left/right' functions.
It's so important to have proportional control of your rc airplane, as this ensures accurate control. And bear in mind that most radio control planes will respond to the slightest control surface deflection - just a few millimeters deflection will be enough to change the plane's path through the air.
Understanding your rc airplane controls, or indeed the controls of any rc model, is of paramount importance if you want to enjoy your model to its fullest and get the most out of the hobby.
Always take a bit of time to understand how your new rc airplane, helicopter or vehicle is operating and responding to your transmitter inputs, rather than just moving a stick and watching the model change direction. You'll be a much better rc'er for it!
